The Logarithmically-non-uniform Helix Antenna Mounted Above a Finite Ground Plane
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.11113/elektrika.v21n1.341Abstract
In this paper the influence of ground plane size on the performance characteristics of a thin-wire helical antenna characterized by a logarithmically varying turns spacing, and mounted above a circular ground plane of finite extent, is systematically investigated. The moment-method formulation utilized in the paper involves a wire-grid model for the ground plane as well as explicit expressions, deriving from a vector potential approach, for the radiation fields of this ‘loghelix’. Subsequent computational results obtained for a candidate 8-turn ‘loghelix’ axial-mode ˀantenna using various combinations of ‘logarithmic variation factor’ and ground plane size, very clearly reveal that limiting the size of the ground plane to finite dimensions significantly improves antenna performance. Maximum gain obtainable, for example, emerged as 16.45dBi when a finite ground plane is utilized, as against 13.55dBi for the corresponding antenna, backed by an infinite ground plane. The associated axial ratio performance is characterized by 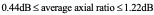 for the finite ground case, and
for the finite ground case, and 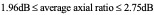 , for the infinite ground plane case. A notable finding of the investigations is that the dip that typically features in the power gain profiles of antenna structures backed by finite ground planes will be eliminated, when ground plane size, relative to antenna size exceeds a certain minimum.
, for the infinite ground plane case. A notable finding of the investigations is that the dip that typically features in the power gain profiles of antenna structures backed by finite ground planes will be eliminated, when ground plane size, relative to antenna size exceeds a certain minimum.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright of articles that appear in Elektrika belongs exclusively to Penerbit Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (Penerbit UTM Press). This copyright covers the rights to reproduce the article, including reprints, electronic reproductions, or any other reproductions of similar nature.
















